Summary:
Use-case prompt suggestions show how to effectively prompt AI tools. They aid learnability and creativity, helping users explore what AI tools can do.
Use-case prompt suggestions are intended to help users understand what they can use the AI tool for and how to interact with it. When designed well, they set accurate expectations for the system and guide users toward effective prompting.
Defining Use-Case Prompt Suggestions
Use-case prompt suggestions are examples of good AI prompts. They are displayed within most AI tools, usually (but not only) to novice users.
Unlike other types of prompt suggestions, which focus on continuing a conversation (followup suggestions) or helping users complete the prompt (prompt autocomplete), use-case prompt suggestions aim to support learnability — helping users quickly understand what the genAI tool can do for them and how.
Designing Use-Case Prompt Suggestions: Simple vs. Complex
Use-case prompt suggestions vary widely in complexity — from short phrases or single-sentence examples to rich, realistic formats like entire conversations, images, or videos that show full user–system interactions.
Choosing the right level of complexity depends on several key factors:
- How broad or specialized the AI system’s capabilities are
- How familiar users are with AI in general
- The complexity of the typical tasks users perform
- Where in the interface the prompt suggestion appears
Simple, clickable prompts placed inside or near the input field work well for broad systems and low-complexity tasks.
Complex prompt suggestions are better suited for specialized systems and high-complexity tasks, where rich examples provide more meaningful guidance.
While users are more likely to engage with quick, actionable prompts, rich examples can help them develop a deeper understanding of how to interact with the system effectively.
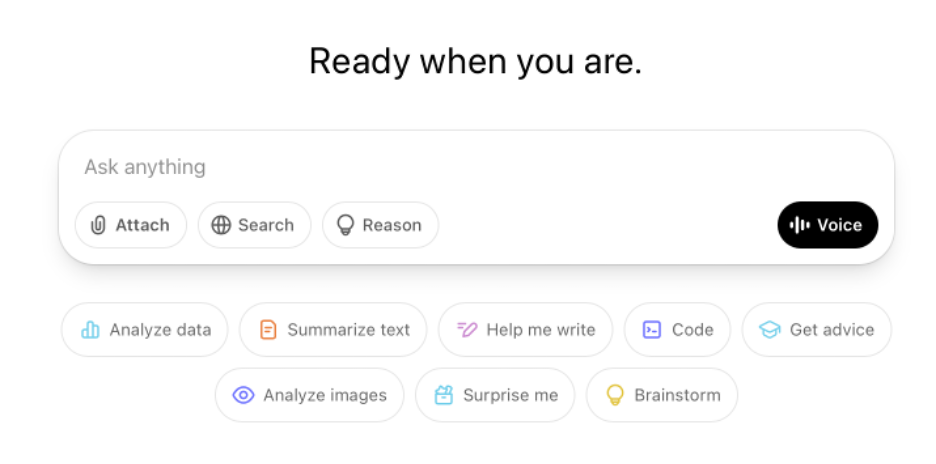
Prompt complexity also affects how suggestions should be displayed. Simple prompts take up little space, allowing multiple suggestions to be shown at once. This is ideal for inline layouts or suggestion lists.
Complex prompts, however, require more screen real estate and are better presented one at a time, such as in a carousel, expandable section, or example library.
Ultimately, designers must balance two competing goals when choosing the complexity and format of prompt suggestions:
- Helping new users quickly understand what the system can do
- Teaching and inspiring active users to use the system effectively
Helping New Users Quickly Understand What the System Can Do
The primary goal of helping users understand what an AI tool or feature can do is to encourage them to start using it and ultimately increase adoption. This is especially important for unauthenticated users, as organizations hope to convert them into long-term, paying customers.
At this stage, users are typically:
- Just discovering the tool
- Exploring its capabilities
- Deciding whether to register, try it out, or subscribe
To support this last decision, companies often display simple, curated examples in the preauthentication view. These static suggestions act as marketing nudges: they are quick to scan, easy to understand, and designed to clearly communicate the tool’s key capabilities, ideally motivating users to create an account and get started.
Highlight Key System Capabilities
For curated use-case prompt suggestions to be effective, their content must be tailored to the user’s level of experience and likely objectives. This alignment helps showcase the AI system’s capabilities in a way that feels relevant and actionable, while also setting realistic expectations for interaction.
A critical consideration is deciding which strengths of the AI system to highlight. Depending on the tool’s purpose and audience, prompt suggestions might emphasize abilities such as:
- Content creation
- Problem solving
- Ideation
The features showcased should reflect potential users’ most common goals. The more closely these suggestions align with user needs, the more likely they are to drive engagement and convert new visitors into active users.
While most AI tools support a wide variety of use cases, it’s the product team’s responsibility to identify a focused set of high-impact capabilities. Highlighting the most broadly relevant strengths ensures that the prompt suggestions appeal to the largest possible share of users — especially in early interactions like the preauthentication experience.
Showcase Functionality with Minimal Friction
These curated examples often function as push revelations — predefined content shown proactively, regardless of user context. While useful for showcasing features, push revelations have well-documented usability pitfalls: they can be intrusive, easily ignored, and quickly forgotten. If these suggestions disrupt rather than assist, they risk undermining their intended purpose.
To be effective, prompt suggestions in preauthentication views should follow the same usability principles as other types of onboarding. They must be:
- Easy to dismiss
- Visually unobtrusive
- Clearly tied to common user goals
Used thoughtfully, these static prompts can serve as lightweight introductions to system capabilities. But if overdesigned or poorly timed, they may frustrate users rather than support them.
Common UI Patterns for Prompt Suggestions Before Login
There are several ways to visually present prompt suggestions in preauthentication views, each offering distinct advantages and tradeoffs.
Pills
Pills are often used to display prompt suggestions as single terms or short phrases. This format is ideal for highlighting a wide range of topics or system capabilities, helping users quickly understand what the AI tool can do.
Pills should be interactive — either triggering the prompt directly or inserting a longer prompt into the input field for users to edit before submitting. In preauthentication views, clicking a pill typically leads users to sign in or create an account to continue, in case they must be logged in to use the tool.
Cards
Using cards to display use-case prompt suggestions allows for in-depth examples of how to interact with the system. Using cards for prompt suggestions works well when:
- The AI tool is specialized or primarily used for a small number of tasks.
- Longer prompts are needed to showcase the system’s capabilities.
Like pills, cards should be clickable and direct users to sign in or create an account (if required).
Videos
Videos are a powerful way to demonstrate how a system works and educate users on its capabilities and interaction patterns. They’re especially useful when users have little to no prior experience with generative AI tools, as they can offer rich context and realistic examples of effective usage.
Carousels
Using a carousel is an effective way to showcase multiple curated examples of how to interact with the system. It offers both breadth and depth — allowing users to see a variety of use cases while presenting each one individually. Carousels make it easy to highlight complex interactions and rich examples of the system’s capabilities.
Claude: Displaying Multiple System Abilities in a Carousel
One example of this approach is Claude’s preauthentication view, which included a curated carousel showcasing four examples of what the system could be used for. The examples highlighted the system’s ability to:
- Visualize data
- Organize content
- Analyze data and create a report
- Optimize code
Showcasing Claude’s broad abilities makes sense, given that its millions of users likely have a wide variety of goals. Featuring a selection of curated use-case prompt suggestions in the preauthentication view effectively highlighted what the AI could do and helped set realistic expectations for how users can interact with it.
However, Claude’s design team has had to sacrifice realistic prompt and interaction examples in order to convey the system’s capabilities quickly. For example, one of the prompt suggestions reads:
Claude, make a content calendar for my marketing campaign.
To which Claude simply responded, Of course! Here’s the calendar! and provided a complete-looking output. This is not a realistic representation of how someone would create such an output using Claude.
Instead, they’d probably need to have a much longer conversation with Claude to achieve their intended result. But this is a tradeoff to consider when designing use-case prompt suggestions to quickly highlight the system’s abilities.
Teaching and Inspiring Active Users to Use the System Effectively
Once users are authenticated and actively engaging with the AI system, the focus of prompt suggestions shifts from introducing capabilities to supporting ongoing use. At this stage, the primary goals are to:
- Help users complete tasks more efficiently
- Accelerate workflows
- Encourage deeper engagement
- Inspire new ways to interact with the system
- Increase user satisfaction and retention over time
To achieve these goals, AI systems can not only use curated examples but also surface system-generated prompt suggestions during user interactions. These appear in real time and are tailored to the current context, offering just-in-time guidance and relevant next steps.
Contextually Relevant Prompt Suggestions
To truly support users and provide value, system-generated prompt suggestions must be context-aware. This means they should:
- Adapt to the specific situation the user is in
- Appear at the right moment, ideally when users need guidance or inspiration
- Offer relevant suggestions that help users move forward, complete tasks, or make decisions
By meeting users where they are in the experience and offering timely, specific, and meaningful prompts, designers can not only improve efficiency but also foster continued exploration and trust in the system. Over time, this contributes to stronger engagement and higher retention among active users.
Context-aware prompt suggestions are especially valuable in two common scenarios:
1. When Users Face High Ambiguity
Ambiguity arises when users are unsure how to proceed or what to focus on, often due to many possible directions.
For instance, consider a user planning a trip to Miami, Florida on Tripadvisor.com. Once they arrive on the site, they’re faced with countless options — hotels, activities, restaurants, beaches, nightlife — all competing for attention. Without clear guidance, it can be difficult to know where to begin.
To reduce this ambiguity, Tripadvisor’s AI assistant surfaced relevant, situational prompt suggestions like:
- Which hotels in Miami have ocean views?
- What are the best rooftop bars in Miami?
- What are the best beaches in Miami?
- Where can I find live music in Miami?
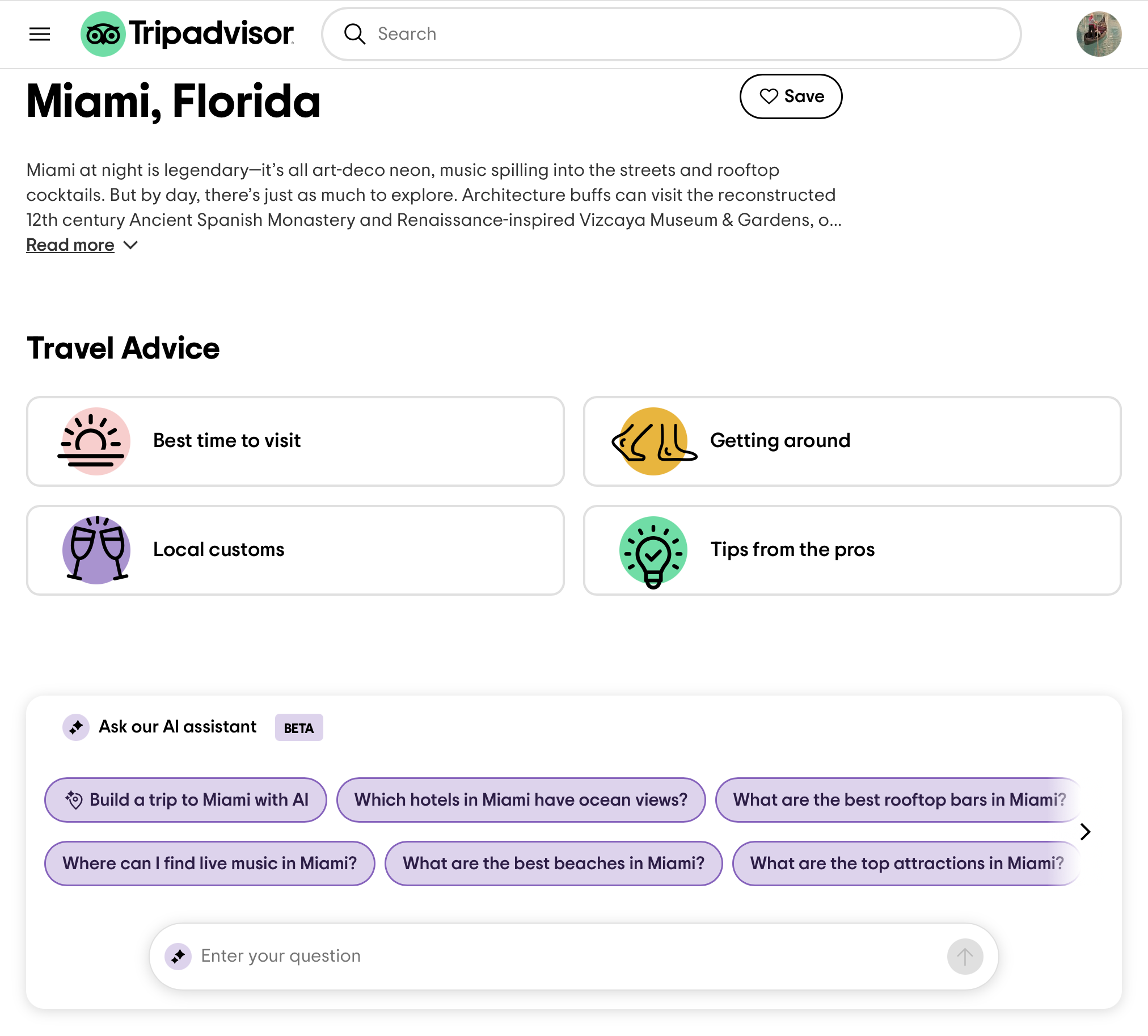
Such suggestions provide focused entry points into the planning experience. They reduce cognitive load by surfacing relevant, location-specific queries at the right moment. Instead of sifting through endless possibilities, users are nudged toward prompts that match their interests and context, helping them move forward with clarity and confidence.
2. When Users Lack Domain Knowledge
Another situation where context-aware prompt suggestions add value is when users are unfamiliar with a topic or product category. In these cases, users may not have the language, context, or mental model to know where to begin. This is common in ecommerce scenarios where users evaluate complex or unfamiliar items.
Imagine someone shopping for a home generator for the first time. They might not know which features matter most — wattage, fuel type, noise level, or portability — or what tradeoffs to consider. Without domain knowledge, it’s hard to know what questions to ask, even if the site offers AI-generated summaries or a product-review chatbot.
Context-aware prompt suggestions can bridge this gap by surfacing relevant questions like:
- What do reviewers say about reliability during power outages?
- Is it easy to move around?
- Does it have an automatic shutoff?
- What kinds of fuel does it work with?
- How loud is it compared to other generators?
These targeted suggestions help users navigate unfamiliar territory, spotlight important product dimensions, and build confidence in their decision, even if they start with little expertise. By anticipating common concerns and aligning prompt suggestions with user goals, friction can be removed and shopping experiences improved.
Case Study: Amazon’s Rufus AI Dynamically Adapts Prompts to Product Context
Amazon’s Rufus AI chatbot illustrates how context-aware prompt suggestions can be applied in practice. When a user reviewed Birkenstocks, Rufus adapted to the specific product and provided situationally relevant prompt suggestions such as:
- Do Birkenstocks come in both narrow and wide?
- Which Birkenstock sandals are best for arch support?
- Are Birkenstock clogs good for standing all day?
- Do Birkenstocks require a break-in period?
This approach combines both contextual awareness and anticipation of user needs, reducing uncertainty and helping users uncover relevant product information quickly.
Specific Beats Vague: Why Precision Matters in Prompt Suggestions
Broad or generic prompt suggestions are rarely effective, even when the goal is to inspire new users or showcase what the AI system can do, as these vague prompts often lack the clarity users need to evaluate whether they are useful.
In contrast, specific and targeted suggestions help users quickly determine relevance and are more likely to lead to meaningful interaction.
Good Example: Instacart’s Targeted Search Prompts
Instacart provided a strong example of how specificity can improve the user experience. When users interacted with the search feature, the system surfaced clear, focused suggestions, rather than showing general categories. For example, they included phrases like:
- Easy family dinners
- Nutritious snacks for kids
- Easy dinner ideas
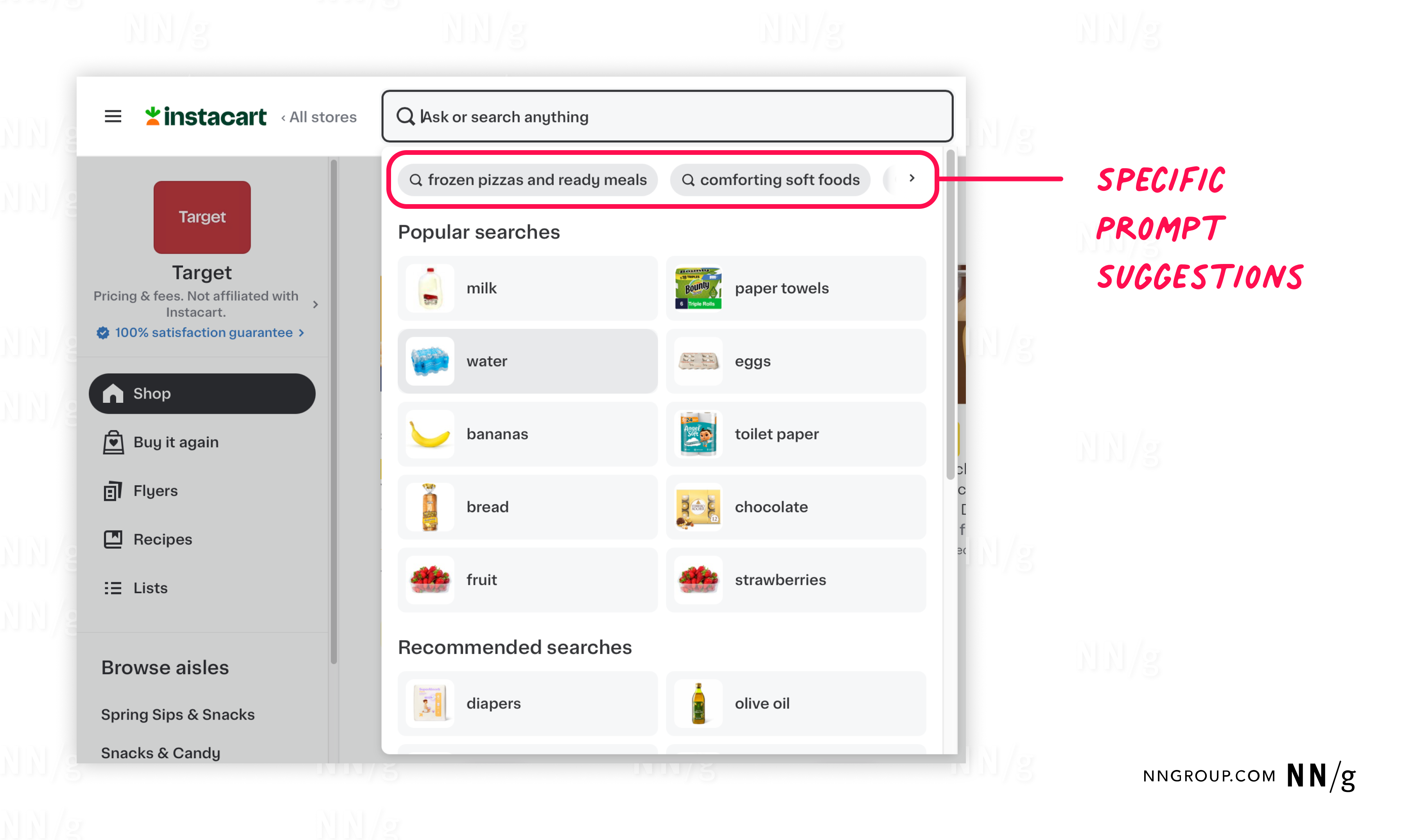
These prompts included enough detail for users to immediately understand their purpose and value. One user captured this sentiment well:
“This is more pointed: Easy family dinner ideas — fantastic! Nutritious snacks for kids, Easy dinner ideas — these are extremely helpful buzzwords for me.”
By using concrete, situationally relevant language, Instacart’s prompts made it easier for users to decide how to proceed and increased the chances of engagement.
Individualization Increases Relevance and Value
Prompt suggestions become more useful when they are tailored to the individual user. Instead of offering the same prompts to everyone, systems that adjust to a user’s specific context, such as their level of expertise, browsing behavior, or previous interactions, can provide suggestions that feel much more relevant and helpful.
For example, in a project-management app, the system can adapt based on how familiar someone is with the tool:
|
Product: Project-Management App |
||
|
User Journey Stage |
Meaningful Prompt |
Prompt Purpose |
|
New user |
How do I create my first project? |
Help them get started and understand the basics. |
|
Intermediate user |
How do I set up task dependencies between team members? |
Support more advanced planning and coordination. |
|
Experienced user |
How can I automate recurring tasks in this workspace? |
Enable efficiency and deeper use of advanced features. |
By matching the complexity of the prompt to the user’s skill level, the system reduces friction, surfaces relevant functionality, and increases the likelihood of meaningful engagement.
This type of individualization can be based on:
- Previous conversations with the AI
- Past browsing or search behavior
- Account history or saved preferences
These inputs help the system present focused and timely suggestions that align with the user’s goals.
When Personal Data Isn’t Available: Learn from Others
In situations where the system doesn’t have enough information about the current user, such as during a first-time visit or an anonymous session, it can still offer helpful suggestions by looking at patterns from other users.
For example, the system might:
- Show popular searches related to the current topic
- Highlight common tasks completed by others in similar contexts
- Suggest prompts that other users have found useful in the same area
While these suggestions aren’t personalized to the individual, they are still grounded in real user behavior. They reflect what has helped others in similar situations and give new users a strong starting point.
Increase Engagement by Placing Prompt Suggestions Near the Input Field
For prompt suggestions aimed at teaching or inspiring active users, placement is just as important as content. To support usability and maximize engagement, suggestions should be positioned near the text input field — the primary focus of user attention during interaction with an AI system.
The input field serves as the main entry point for user queries. Whether a user is preparing to type or waiting to respond, their attention is naturally drawn to this area. Placing suggestions in close proximity to this field ensures they are noticed at the exact moment users are most likely to engage with them.
The format of these suggestions also plays a key role in usability. Two commonly effective formats are:
- Pills: Short, clickable phrases or questions. Their compact design makes them easy to scan and ideal for surfacing multiple lightweight suggestions without overwhelming the interface.
- Cards: A more spacious format that allows for longer prompts, brief descriptions, or supporting visuals. Cards are especially useful when additional context is needed to help users understand the suggestion.
Both formats should support direct interaction, allowing users to insert a prompt with a single click or tap. This design minimizes interaction cost, particularly for users who are uncertain about what to ask or how to phrase their request.
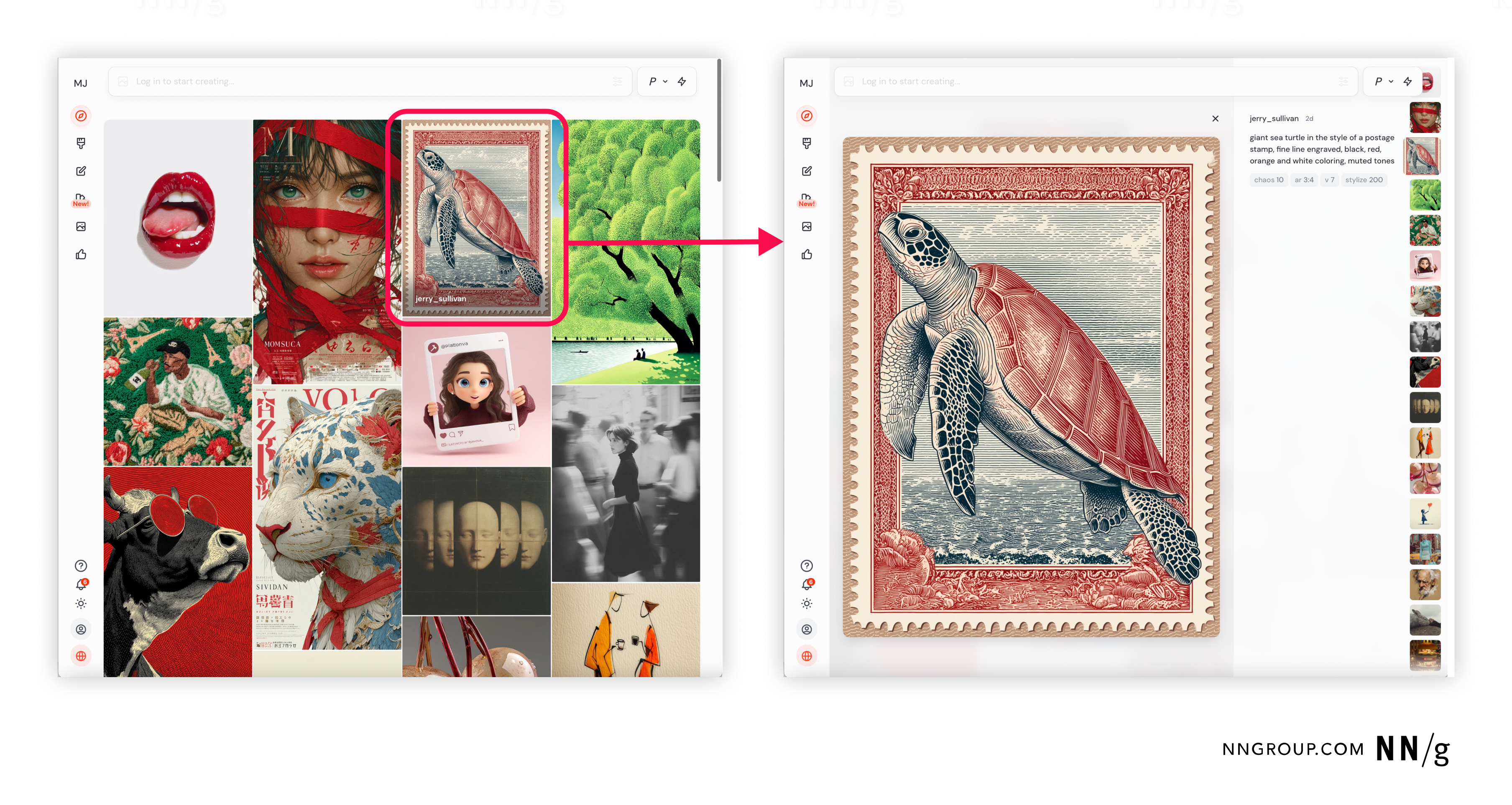
Use an Example Library When More Context Is Needed
When users need more information or context to understand how to interact with an AI system, example libraries can be an effective option. These libraries offer a curated collection of prompts paired with outputs, providing both practical guidance and creative inspiration.
By showcasing full examples, they help users grasp what’s possible with the system and how to phrase their requests to get meaningful results. This is particularly valuable for systems with complex capabilities or for users who are still developing mental models of how the AI works.
Example libraries are especially common in generative AI tools for visual content, such as image or video creation. In these cases, the visual nature of the examples makes the system’s capabilities immediately clear. This approach not only supports new users during onboarding but also keeps experienced users engaged by offering fresh ideas and use cases.
Use Human Oversight to Ensure Relevance and Appropriateness
The examples shown are often based on real user inputs and outputs. However, most product teams should actively select and curate these examples, rather than auto selecting them from recent activity.
Manual selection helps maintain a high standard of quality and ensures that all examples align with the brand’s tone, purpose, and values. It also helps avoid displaying inappropriate or off-brand content, such as politically sensitive or overly sexualized material.
Use Analytics to Optimize Prompt Suggestions
Analytics can play a critical role in helping product teams refine and improve the effectiveness of use-case prompt suggestions.
There are two primary ways analytics can support this effort:
- Identifying common use cases. Usage data can reveal which tasks or goals are most frequently pursued by current users. These insights can inform which prompt suggestions to display to new users, ensuring that suggestions reflect real-world behaviors and needs.
- Evaluating prompt performance. Analytics can also show which prompt suggestions users engage with the most and which are consistently ignored. This information helps teams make data-informed decisions about which suggestions to keep, improve, or remove.
However, it’s important to interpret these metrics with care and be aware of confounding factors. Engagement rates are often influenced by placement, not just content. For example, suggestions shown first in a carousel or positioned near the input field are more likely to be clicked than those located deeper in the interface or behind a More button.
To reduce this bias and get a clearer picture of what users find useful, consider randomizing the order in which prompt suggestions are displayed. This approach will allow teams to isolate the impact of content from position, leading to more accurate optimization decisions.